|
Are you struggling to find the datasheet for a specific Integrated Circuit (IC)? Don't worry, we've got you covered! In this article, we'll show you some of the most effective methods to find the datasheet for an IC.
Method 1: Check the Manufacturer's Website The first place you should look for an IC datasheet is the manufacturer's website. Most IC manufacturers provide datasheets for their products on their website, either in the form of a downloadable PDF or an online document. Simply search for the IC you're interested in on the manufacturer's website, and you should be able to find the datasheet in no time. Method 2: Use Datasheet Search Engines If you're unable to find the datasheet on the manufacturer's website, you can try using a datasheet search engine. These search engines are specifically designed to help you find datasheets for electronic components, including ICs. Some popular datasheet search engines include Datasheets360, Octopart, and Digi-Key. Simply enter the part number of the IC you're interested in, and the search engine will provide you with a list of relevant results. Method 3: Look on Distributor Websites In addition to the manufacturer's website and datasheet search engines, you can also try looking for the datasheet on distributor websites. Distributors such as Mouser, Newark, and Arrow Electronics often provide datasheets for the products they sell. Simply search for the part number of the IC you're interested in on the distributor's website, and you should be able to find the datasheet in the product information section. Method 4: Ask for Help on Online Forums If you're still unable to find the datasheet for an IC, you can try asking for help on an online forum. There are several online forums dedicated to electronics, and many members of these forums are experts in the field. Simply post a question asking for help finding the datasheet for the IC you're interested in, and someone should be able to point you in the right direction. In conclusion, there are several ways to find the datasheet for an IC, including checking the manufacturer's website, using a datasheet search engine, looking on distributor websites, and asking for help on an online forum. By using these methods, you should be able to find the information you need quickly and easily. So, start your search now and get the datasheet you're looking for!
0 Comments
In the automotive industry, electronic control units (ECUs) are used to manage a wide range of functions, from engine control to safety systems. These ECUs rely on microcontrollers (MCUs) to perform their tasks. One of the most common types of MCUs used in automotive applications is the BOSCH ECU MCU A/D.
Types of BOSCH ECU MCU A/D BOSCH offers several types of ECU MCU A/D, including the C16x, M16C, and M32C families. These MCUs differ in their performance, power consumption, and features. The C16x family is designed for high-performance automotive applications, with a maximum clock speed of up to 40 MHz. These MCUs feature a 16-bit architecture and offer a range of peripherals, including timers, ADCs, and communication interfaces. The M16C family is designed for mid-range automotive applications and features a 16-bit architecture with a maximum clock speed of up to 32 MHz. These MCUs also offer a range of peripherals, including timers, ADCs, and communication interfaces. The M32C family is designed for low-power automotive applications and features a 32-bit architecture with a maximum clock speed of up to 40 MHz. These MCUs offer similar peripherals to the C16x and M16C families but consume less power. How BOSCH ECU MCU A/D Works BOSCH ECU MCU A/Ds are based on a Harvard architecture, which separates program memory and data memory. This architecture allows for faster execution of instructions and data transfer between the two memory spaces. The MCUs also feature a built-in analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which allows them to read analog signals from sensors. The ADC converts the analog signal into a digital value that can be processed by the MCU. The MCUs also include a range of peripherals, including timers, communication interfaces, and pulse-width modulation (PWM) generators. These peripherals allow the MCU to perform a range of tasks, such as controlling the speed of a motor or communicating with other systems. Examples of BOSCH ECU MCU A/D Use BOSCH ECU MCU A/Ds are used in a wide range of automotive applications, from engine control to safety systems. For example, they can be used to control the fuel injection timing in a gasoline engine or the ignition timing in a diesel engine. They can also be used to manage safety systems, such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and airbag systems. The MCU can read sensor data from the ABS system to determine when to activate the brakes to prevent wheel lockup. It can also read data from the airbag system to determine when to deploy the airbags in the event of a collision. Infineon and Motorola MCU Types In addition to BOSCH ECU MCU A/Ds, Infineon and Motorola also offer MCUs for use in automotive applications. Infineon offers several families of MCUs, including the TriCore and Aurix families. These MCUs feature a 32-bit architecture and offer high-performance and safety-critical features. The TriCore family is designed for general-purpose automotive applications, while the Aurix family is designed for safety-critical applications, such as airbag and brake systems. Surface-mount device (SMD) components are integral to modern electronics manufacturing, as their compact size and convenience make them a popular choice for manufacturers. Properly identifying and testing SMD components is critical for electronics professionals to ensure that their circuits function correctly. Types of SMD Components SMD components come in various types, each serving a specific purpose in electronic circuits. The following are some of the most common types:
Identifying SMD Components Accurately identifying SMD components can be a challenging task, particularly for beginners. However, several techniques can help identify them precisely:
Testing SMD Components After identifying an SMD component, it is crucial to test it to ensure proper functioning. Here are a few techniques for testing SMD components:
SMD components are essential to the modern electronics industry, and accurately identifying and testing them is critical for professionals to ensure that their circuits operate correctly. By employing the techniques outlined in this article, electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike can confidently identify and test SMD components, guaranteeing optimal circuit performance. Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical energy and release it when needed. They are commonly used in a wide range of electronic devices, including televisions, computers, and air conditioners. However, like any other electronic component, capacitors can sometimes fail and need to be replaced. In this article, we will discuss the different types of capacitors, how to test them, and how to replace them.
Types of Capacitors There are several different types of capacitors, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of capacitors include:
Testing Capacitors If you suspect that a capacitor has failed, you can use a multimeter to test it. Here are the steps to follow:
Replacing Capacitors Replacing a faulty capacitor is a relatively simple process that can be done with a few basic tools. Here are the steps to follow:
Capacitors are an important component in many electronic devices, and it is important to know how to test and replace them when necessary. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure that your electronic devices are working properly and avoid costly repairs or replacements. Coils and inductors are fundamental passive components in electronic circuits, playing a vital role in a wide range of applications, from power electronics to radio communication. In this article, we will explore the various types of coils and inductors, methods to test them, and their critical applications.
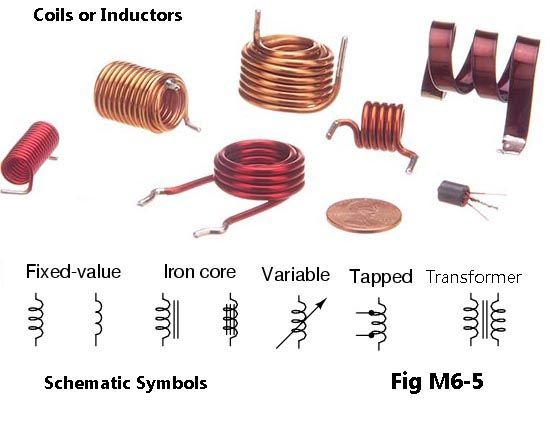
Coil Overview A coil is an electromagnetic device that generates a magnetic field when an electrical current passes through it. The most common type of coil comprises a conductor, such as copper wire, wrapped around a core material, such as iron, ferrite, or air. The core material is selected based on the application requirements, including the desired inductance, operating frequency, and other parameters. Types of Coils There are three primary types of coils used in electronics: solenoid coils, toroidal coils, and air core coils. Solenoid Coils Solenoid coils are used in applications where electrical energy is converted to mechanical energy. A solenoid coil comprises a wire wrapped around a cylindrical core that creates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. The magnetic field causes the core to move, which produces a mechanical force. Toroidal Coils Toroidal coils are widely used in power supplies and radio frequency circuits. They consist of a wire wrapped around a doughnut-shaped core, providing high magnetic coupling and low electromagnetic interference (EMI). Due to their compact size and high efficiency, toroidal coils are ideal for applications where space is at a premium. Air Core Coils Air core coils are used in applications that require high-frequency signals, such as radio transmitters and receivers. Air core coils consist of a wire wrapped around a non-magnetic core, such as plastic or ceramic. Due to the absence of a magnetic core, air core coils offer low inductance but provide high Q-factor and low signal loss. Inductor Overview An inductor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electrical current flows through it. An inductor comprises a coil of wire wrapped around a core, which can be made of various materials, including iron, ferrite, or air. Types of Inductors There are several types of inductors used in electronics, including fixed inductors, variable inductors, and surface mount inductors. Fixed Inductors Fixed inductors are the most commonly used type of inductor in electronic circuits. They have a fixed value of inductance, determined by the number of turns in the coil and the core material. Fixed inductors can be made of a range of materials, including ceramic, ferrite, and iron powder. Variable Inductors Variable inductors, also known as tuning coils, are used in radio frequency circuits to tune the frequency of a signal. A variable inductor comprises a coil of wire wrapped around a core, which can be rotated to change the inductance value. Variable inductors are commonly used in radio receivers and transmitters to adjust the frequency of the signal. Surface Mount Inductors Surface mount inductors are compact and are commonly used in modern electronic circuits, where space is at a premium. Surface mount inductors are small in size and can be mounted directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB), eliminating the need for additional wiring. Testing Coils and Inductors Testing coils and inductors is essential to ensure that they meet the required specifications. The most common method of testing is to use an inductance meter, which measures the inductance value of the component. A multimeter can also be used to test the continuity of the coil or inductor. Applications of Coils and Inductors Coils and inductors are used in a wide range of electronic circuits, including: MorePower Electronics Coils and inductors are used extensively in power electronics to store and transfer energy. In applications such as transformers and chokes, inductors are used to smooth out the current flow and reduce the amount of ripple in the output voltage. They are also used in switch-mode power supplies to store and release energy, resulting in more efficient power conversion. Radio Communication Coils and inductors are essential components in radio communication systems, where they are used to filter and tune radio frequency signals. In applications such as radio receivers and transmitters, inductors are used to match the impedance of the input and output circuits, improving signal strength and reducing interference. Automotive Electronics Coils and inductors are used extensively in automotive electronics, where they are used to filter and regulate the electrical power. They are used in ignition systems, power steering, and fuel injection systems to ensure that the electrical power is delivered efficiently and reliably. Medical Devices Coils and inductors are used in medical devices, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, where they are used to generate magnetic fields. In MRI machines, coils and inductors are used to create a strong magnetic field that aligns the protons in the patient's body, allowing for high-resolution images to be produced. Coils and inductors are fundamental passive components in electronic circuits, providing critical functions such as energy storage, signal filtering, and impedance matching. Understanding the various types of coils and inductors, how to test them, and their applications is essential to design and build efficient and reliable electronic circuits. By selecting the right coil or inductor for the application, designers can optimize their circuits for performance, efficiency, and cost. |
Auto Tuning Blog “The content provided is for educational and informational purposes only.”
Categories
All
|
Please note that we don't accept Orders / support requests sent direct to our email address.
Electronic Repair Company |
|
|
All Rights Reserved, ©2024 Electronic Repair Company